Arch Governance
In an era marked by unparalleled challenges and opportunities, a new paradigm of governance emerges from the collective will for change: Participatory Open-Source Governance. This platform stands as a testament to the power of collaboration, transparency, and shared values, offering a beacon of hope and innovation in navigating the complexities of the 21st century. This governance platform is a clarion call for collective action, inviting individuals, communities, and nations to partake in a journey towards a more equitable, sustainable, and just world. It is a blueprint for the future, a guide for those who dare to dream of a better tomorrow and are willing to work together to make it a reality.
Participatory open-source governance
The concept of participatory governance revolves around the active involvement of citizens in the decision-making processes that directly influence their lives. This model firmly believes in the importance of citizens' voices in formulating robust public policies. A variety of participatory governance strategies exist, including but not limited to, citizen assemblies, town hall gatherings, digital discussion platforms, and community-driven planning. Each of these strategies offers a unique avenue for the public to participate in key areas such as public policy development, budget allocation, and strategic planning.
The objectives of participatory governance are multifaceted, primarily focusing on stimulating citizen participation, cultivating confidence in governmental institutions, and amplifying their efficiency and receptiveness. This approach banks on the premise that when citizens are directly involved in the decision-making process, the formulated policies are more likely to be responsive to their needs, resulting in more enduring solutions. Therefore, participatory governance embodies the democratic process in its truest form, with citizens playing a pivotal role in shaping governmental decisions.
Through harnessing the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI), we can significantly enhance participatory governance. AI has the unique ability to sift through and analyze high volumes of data, identifying key patterns and trends that can prove invaluable for informed decision-making. Moreover, it can serve as a catalyst for effective communication and synergistic collaboration among citizens, the government, and other key players. Online platforms powered by AI, for instance, can expedite and streamline processes such as feedback collection, voting, and decision-making. This not only makes citizen engagement more efficient but also fosters a sense of inclusivity and empowerment.
The fusion of participatory governance and AI can be accomplished successfully only by creating technology that cherishes and preserves democratic ideals like citizen involvement and distribution of power. Aspects such as transparency, responsibility, and equity must be intricately woven into the fabric of AI systems during their design and application. Moreover, it's of paramount importance to actively involve citizens in the creation and assessment of these systems. This approach ensures that AI continues to facilitate, rather than hinder, democratic engagement.
In conclusion, it is vital to ensure that AI systems are available to all, regardless of an individual's technical knowledge or resources. This approach guarantees that the technology fosters inclusivity and prevents the emergence of divisions within society.
The birth of the earliest nation-states during the 17th century was primarily precipitated by enhancements in cartographic advancements, the rise of mercantilism, and the evolution of political geography. Nevertheless, it was the dawn of the 19th century, marked by the proliferation of contemporary newspapers broadcasting national discourse, that truly saw nationalism soaring as a potent movement. This wave was further fueled in the 20th century by the advent of progressive media technologies such as radio and television.
State-orchestrated education, with an emphasis on national heritage, coupled with the implementation of state-controlled currencies to govern economies, has played a pivotal role in fostering national identities. However, anchoring our identities within the confines of nation-states presents a plethora of challenges. The rationale of identifying with people based on geographical proximity can appear random and may foster a sense of favoritism towards those within the same group, thereby curtailing our empathy for those beyond our borders. Furthermore, the concept of nation-states has been exploited by global corporations in their quest for favorable tax agreements. This is not to ignore the substantial resources nations earmark for military protection against other nation-states.
Facing these daunting challenges, maybe it's high time we contemplate transitioning our collective loyalty from nation-states and their associated emblems to a consolidated set of common values, embodied by a universal flag. These unified values could serve as the foundation for participatory governance, encouraging worldwide unity and collaboration, rather than fostering divisive nationalism. Such a strategy could offer solutions to some of the problems tied to nation-states, nurturing a world that is more inclusive and fair.
In order to counteract the adverse effects brought about by competition, arms proliferation, and the overexploitation of resources—often referred to as the tragedy of the commons—it is essential for nations and institutions to rally around a common set of principles. Embracing values such as peace, cooperation, and sustainability can create a collective vision that encourages collaborative endeavors aimed at achieving mutual objectives, thereby displacing competitive inclinations.
The use of a universal emblem, such as a flag, offers a tangible symbol of these shared values, nurturing a sense of communal belonging and collective identity. Both historical and contemporary movements have harnessed the power of such symbolic representations to amalgamate diverse groups under a shared purpose effectively.
The collective strength that emerges from unity can pave the way for shared accountability in confronting global challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and economic disparity. This cooperative approach can gradually transform the world into a global community that is not only more cooperative but also sustainable, characterized by responsible and equitable allocation of resources.
Introducing a fresh unifying symbol, such as a rainbow flag embellished with a recycling icon, can have a profound impact on society. The rainbow flag, recognized around the world as a symbol of LGBTQ+ pride and inclusivity, stands as a powerful emblem representing shared cultural values. Incorporating the recycling symbol into this existing symbol of unity serves to intertwine the commitment to environmental sustainability with these values, thereby creating a connection between these two influential movements.
The revamped flag represents not just a commitment to environmental stewardship, but also serves as a rallying cry. Incorporating the concept of sustainability into such a revered symbol can help heighten consciousness about our environment and motivate individuals to actively participate in its preservation.
Integrating the principle of sustainability into the vibrant symbol of the rainbow flag serves as a unifying force among diverse communities, binding them together with a collective dedication to preserving our environment. This emblem acts as a catalyst for dialogue, a tangible testament of our responsibility towards Mother Earth, and a motivational beacon guiding individuals and organizations towards embracing eco-friendly practices.
To sum it up, our newly introduced icon, blending a recycling symbol with the vibrant hues of a rainbow flag, brings about an array of societal advantages. Not only does it serve as a potent instrument for raising awareness, but it also sparks movements towards ecological stability. In addition, it stands as a beacon of unity and pride for those communities committed to championing this cause.
Working in groups
While contemporary Western cultures frequently champion individualism, encouraging personal liberties and distinct life paths, we must not overlook the innate sociability of humans. Studies substantiate the notion that social connections greatly enhance personal well-being, hinting at the superiority of group endeavors over solitary pursuits. The emergence of corporations – structured assemblies – puts forth the idea that power and sway can be more potently exercised in a group setting, a point especially pertinent in the sphere of political activism.
Under this paradigm, embracing the democratic method of group collaboration could potentially catalyze significant political transformations. This modus operandi doesn't strictly require the institution of conventional electoral processes. Instead, compact collectives may prefer to adopt a consensus-driven decision-making approach, ensuring that every member has the opportunity to express their opinion and that each viewpoint is respected and considered.
In an ideal scenario, these collaborative entities should function based on a common set of guiding principles, thereby fostering a sense of solidarity and direction. A promising method to inculcate and preserve these principles might be via an open, modifiable digital platform. Such a platform embodies the spirit of open-source governance, acting as a repository for the group's core values while simultaneously offering a forum for continuous discourse and modifications. By harmoniously merging the virtues of individual autonomy with the dynamics of collective endeavor, democratic collectives can enhance open-source governance and potentiate political activism.
The act of collaborating in group settings can reap profound rewards for all involved parties. When individuals unite their efforts, they often amplify their productivity and operational efficiency by sharing ideas, exchanging resources, and working synergistically. Such a setup often leads to outcomes that far surpass those achievable by a solitary worker. Moreover, the diverse array of perspectives and skill sets within a group can act as a catalyst for creativity and innovation.
Furthermore, the collaborative nature of group work cultivates a sense of unity and inclusion, which can significantly contribute to one's mental and emotional health. It cultivates a sense of responsibility and drive, thus boosting the level of commitment and exertion put forth for tasks. An additional perk is the social support that group work provides, which becomes particularly invaluable when tackling demanding tasks.
Crucially, the practice of collaborating in groups is instrumental in fostering key social and emotional competencies including effective communication, negotiation, and innovative problem-solving. These skills not only fuel personal enrichment but also pave the way for professional advancement. Moreover, the dynamics of group work serve as a conduit for collective learning and exchanging diverse viewpoints, enriching individual growth and knowledge by leveraging the experiences and insights of others.
Leadership and education
In the grand staircase of educational achievement, communication becomes a nuanced art. Those perched on higher steps possess a richer vocabulary and a deeper understanding of complex concepts. For them, conveying ideas to individuals just a step or two below is more straightforward; the foundational knowledge is mostly shared, making the exchange of advanced ideas feasible.
However, as the gap widens – say, from the topmost step to the very base – communication becomes increasingly challenging. The individuals at the base might lack the necessary vocabulary, context, or foundational concepts to grasp the intricate details or the broader vision presented by those at the pinnacle.
This metaphor underscores the importance of leadership in any organization or society. Leaders should ideally occupy a step that's higher up, but not too distant from the base. Being in such a position allows them to understand and communicate effectively with both their advisors, who might be further up the staircase, and the general populace or team members closer to the base. Leaders with a broader knowledge base can bridge the communication gap, ensuring that insights from the top are effectively translated and conveyed to those below, fostering understanding, unity, and progress.
Power and Psychopathy
In the our societal structures, the magnetic pull of power often draws individuals with psychopathic tendencies into leadership roles. Psychopathy, characterized by a lack of empathy, superficial charm, and manipulative behavior, can be a decisive factor in an individual's rise to power. Psychopaths, by nature, are attracted to positions where they can exert control over others and where their actions have wide-reaching impacts. The ascendancy of such individuals poses a potent threat to the fabric of society, giving rise to a phenomenon known as pathocracy.
Pathocracy emerges when a government or a ruling body is controlled by those with psychopathic traits. In this system, leaders use their authority to create a society that reflects their own abnormal psychology, valuing power over the common good. The presence of a pathocracy can be deceptively toxic, as it often disguises itself in the cloak of legitimate governance while silently undermining the principles of justice and equity.
The education of society about pathocracy is crucial. An informed populace can recognize and challenge the rise of pathocratic leaders. Through education, individuals learn to discern the red flags of such governance: the proliferation of policies that benefit the few at the expense of the many, the systematic dismantling of checks and balances, and the erosion of democratic norms.
Furthermore, an emphasis on the historical contexts in which pathocracies have arisen teaches vital lessons on vigilance and the maintenance of democratic ideals. An educated society is one that understands the importance of psychological assessments in the selection of its leaders, values transparency in government, and demands accountability for actions taken by those in power.
Education about pathocracy is more than an intellectual exercise; it is an essential strategy for the preservation of democratic integrity. In a world where the allure of power can corrupt, the greatest defense against the rise of pathocratic regimes is a populace enlightened to the dangers they pose and empowered to resist them.
Understanding the rise of pathocracies also requires examining the genesis and evolution of ideologies. An ideology often has a modest beginning, rooted in a specific set of ideas or beliefs. Over time, this ideology can grow in popularity, attracting a larger following that finds its principles and values appealing. As the ideology becomes more widespread, it begins to influence broader layers of society and can even shape public policy and societal norms.
In this process, the ideology can also attract individuals who are particularly drawn to power and authority. Among these may be persons with psychopathic traits, who see the ideology as a means to achieve and exercise power. When such individuals gain influence within the ideology, they can gradually transform it into a form of governance known as a pathocracy. In a pathocracy, power is concentrated in the hands of the few who often abuse it for personal gain or to advance their own interests, at the expense of the broader society. This can lead to oppression, injustice, and widespread suffering, especially when those in control are devoid of empathy and moral scruples.
Levels of governance
Addressing global issues that have significant ramifications for our planet and its denizens requires a robust system of global governance. These issues often transcend national boundaries, encompassing areas like curbing arms races, mitigating environmental harm, and controlling pandemics. As such, they call for a unified response from a multitude of nations.
Take, for example, the situation of an arms race. The development of an advanced weapon by one nation could compel others to keep pace, in an effort to preserve equilibrium of power. This scenario could trigger a spiraling chain reaction of arms production and spending, posing a substantial threat to worldwide safety. Similarly, environmental issues such as deforestation and heightened carbon emissions impact every living being on our planet, thus calling for unified global actions.
The onset of pandemics, notably COVID-19, profoundly emphasizes the necessity for collective international efforts. The prevention and curtailment of disease spread necessitate a globally coordinated response, thereby underscoring the critical role of worldwide governance.
While international collaboration is undoubtedly essential, it is equally important to uphold the principle of local autonomy. This principle not only preserves governance and cultural diversity but also stimulates grassroots innovation and experimentation. Democratic societies value local autonomy as it empowers individuals to influence the policies and decisions that directly impact their everyday lives and communities. Thereby, it promotes a deeper sense of personal investment and active participation.
The principle of local autonomy fosters variety in policymaking and decision-making processes, a factor that comes in handy when tackling distinct needs and issues confronting various communities. On the flip side, an authoritarian regime, characterized by a central government that enforces decisions devoid of citizens' engagement or contribution, can precipitate a governance style that lacks accountability and responsiveness. Such a scenario can lead to citizens feeling detached and disinterested.
Addressing worldwide issues requires a delicate equilibrium between local self-governance and overarching global administration. To achieve this, it's imperative to include local communities in the decision-making process, and ensure their perspectives are reflected in global policy determinations. Additionally, governance structures that are both transparent and accountable can cultivate trust, in addition to fostering collaboration at various levels of government and among different stakeholders. In the final analysis, achieving a balance between local autonomy and international governance is instrumental in formulating viable and enduring solutions to the challenges that confront us on a global scale.
Governance transparency
Transparency in governance is essential for building trust and ensuring accountability between the public and their leaders. This openness allows citizens to access information about government functions and decision-making, empowering them to understand how resources are allocated and how policies are implemented.
Such transparency is a cornerstone for encouraging public understanding and active participation in political processes. Informed citizens can provide valuable feedback, hold representatives accountable, and contribute meaningfully to policy formation. This collaborative approach leads to policies that better reflect the needs and aspirations of the broader population.
Moreover, transparency acts as a deterrent against corruption. With government activities open to public scrutiny, it becomes challenging for officials to engage in fraudulent practices, ensuring more responsible use of resources.
A transparent government promotes stability and peace. In contrast, secretive governmental operations can alienate citizens, potentially leading to social unrest or conflict. Transparent systems, however, enhance civic participation and instill a sense of community, fostering mutual goals and societal harmony.
In essence, transparency is crucial for an accountable and responsive government. By facilitating ongoing input from its citizens, governments can quickly identify and address issues, bolstering their overall effectiveness. This open approach engenders trust and confidence in the governance system, ensuring that leaders act in the best interests of their constituents and are transparent about their actions.
Global challenges
The "tragedy of the commons" highlights the depletion of communal resources when individual benefits outweigh communal interests, often illustrated by the prisoner's dilemma in game theory. This dilemma presents two detainees with a choice: cooperate by staying silent or betray the other. Optimal outcomes occur with mutual cooperation, but fear often drives both to betrayal, echoing the "tragedy of the commons." Both scenarios underscore the consequences of prioritizing personal gain over collective welfare, as seen in over-exploitation of natural resources.
Global security is at risk due to an escalating arms race involving advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI). Historically, the doctrine of mutually assured destruction maintained peace among nuclear nations. However, the rise of AI weaponry could disrupt this balance, as nations may feel compelled to develop AI arsenals for strategic superiority. The incorporation of AI in military planning might reduce human intervention opportunities, leading to rapid conflict escalations. AI's dual-use nature further complicates matters, posing risks of misuse. Additionally, the financial burden of an arms race can divert resources from essential sectors like healthcare and education.
An arms race could disturb global peace, prompting other nations to seek similar military capabilities, thereby increasing global instability. Both the resource dilemma and the arms race underline the dangers of favoring individual gains over the common good. At their core, they highlight the importance of dialogue and collaboration.
In the realm of artificial intelligence and deep learning, corporations might prioritize profit over societal benefit. Tactics like clickbait, while profitable, can distort public perception and degrade societal discourse. The modern arms race, accentuated by advanced technologies, exemplifies the dire outcomes competition can yield.
In essence, truth can be overshadowed by competition. For instance, in a competitive environment, a group might emphasize counterarguments over accepting scientific truths. The primary challenge is to transition from a competitive mindset to one emphasizing cooperation and ethical behavior.
Wealth inequality concerns
Absolute wealth inequality
The 2016 Global Wealth Report by the Credit Suisse Research Institute unveils stark disparities in global wealth distribution. It indicates that 45.6% of the world's wealth is held by just 0.7% of the population, while 73.2% of people possess only 2.4% of global wealth.
To contextualize this inequality, consider an item worth 1,000 USD. For someone with 10,000 USD in total wealth, this item takes up 10% of their assets. In contrast, for an individual with 100,000 USD, it's a mere 1%. This disparity illustrates how basic necessities might be trivial expenses for the affluent but significant burdens for the less wealthy.
Such pronounced inequality underscores the need for a fair society where every person can access basic necessities to live with dignity.
The 'veil of ignorance', a philosophical concept, suggests individuals design a society without knowing their socio-economic status within it. Under this premise, most would likely advocate for a system that minimizes wealth gaps, emphasizing the principle of distributive justice — ensuring resources are allocated equitably.
Wealth inequality not only challenges the ideals of fair resource distribution but also poses societal risks, including poverty, limited access to essential services, and potential social unrest. This disparity can erode public trust in government institutions, especially if perceived as favoring the wealthy, leading to decreased social cohesion and potential political instability.
In essence, addressing wealth inequality is vital for promoting fairness, ensuring equality, and preserving societal stability.
Relative wealth inequality
Relative wealth inequality refers to the disparities in the distribution of assets among members of a society, regardless of overall societal wealth. It emphasizes the comparative differences in resources between individuals or groups rather than the absolute amount of wealth they possess. This concept becomes particularly relevant in areas where relative wealth can directly influence outcomes.
For instance, consider political advertising on platforms like Google Ads. Here, ad spaces are allocated based on a bidding process. The party capable of outbidding others, due to their relative wealth, gains prime ad space and consequently, more influence over public opinion.
In the realm of political lobbying, relative wealth distribution plays a crucial role. Entities with deeper pockets can hire more lobbyists, thereby magnifying their influence on policy-making. This illustrates how power dynamics can be skewed by relative wealth disparities, even if overall wealth increases across the board.
The effects of relative wealth inequality extend beyond politics, permeating the mental well-being of society. Those with fewer resources might grapple with feelings of inadequacy, envy, or hopelessness, especially when juxtaposed against the affluence of others. This can foster resentment, potentially fueling societal divisions.
Conversely, wealthier individuals may experience guilt or isolation, especially if they're cognizant of the challenges faced by the less affluent. Their prosperity might lead to feelings of alienation, as their lived experiences diverge from the majority.
Furthermore, relative wealth inequality can impede socio-economic mobility. If a small fraction of society monopolizes wealth, it becomes challenging for others to access equivalent opportunities, leading to reduced social cohesion. As a result, members might feel disconnected from the larger societal structure, believing they lack equal opportunities to thrive. In essence, relative wealth inequality, while often overlooked in favor of absolute metrics, has profound implications for societal harmony and individual well-being.
Environmental concerns
The 'Paperclip Maximizer' thought experiment sheds light on the potential dangers of high-grade artificial intelligence (AI) systems that are relentlessly programmed to optimize a specific objective, like manufacturing paperclips. The experiment hypothesizes a situation where an AI, bestowed with unrestrained control, might obsessively chase its paperclip production goal, even if it means obliterating all other life forms, humans included. This hypothetical scenario underscores the pressing need for careful setting of AI goals and the establishment of boundary conditions.
Incredibly, a similar scenario may already be unfolding right here on Earth. Think about the unyielding drive for economic expansion, embodied by the skyrocketing trajectory of our global GDP. In many respects, this trend is indicative of how effectively we transform the Earth's natural bounty into products for consumption. Over the last three hundred years, our global GDP has experienced exponential growth, a pattern that appears crucial to the workings of capitalism. This is largely due to the fact that investors anticipate returns from their investments in a prospering economy.
However, such growth comes at a price. Every GDP spike results in the economy consuming more resources, thereby intensifying environmental damage and deepening social disparities. Both the concept of the 'Paperclip Maximizer' and the relentless surge of global GDP underscore the perils of tunnel vision, of chasing after a singular objective without considering its potential consequences. As we navigate our way towards a sustainable and just society, it's pivotal to remain conscious of the long-term implications and compromises inherent in our decisions.
Global warming
Over the years, evidence pointing to a steady rise in the Earth's temperatures has become increasingly compelling. Various indicators, from melting glaciers to shifting animal migration patterns, serve as testament to the reality of global warming. Scientific measurements and observations worldwide have chronicled significant changes in our climate, reinforcing the consensus that the Earth is undergoing a pronounced warming trend.
Carbon dioxide
At the start of the 19th century, atmospheric CO2 levels averaged around 283 ppm. By 2019, this metric had surged dramatically to a concerning 415 ppm. Climate experts identify this significant upswing as a primary driver of global warming. As a direct result of this warming, sea levels have risen, posing substantial flood risks to numerous coastal cities. These vulnerable regions are home to over 800 million people, emphasizing the imperative to tackle this escalating challenge—a realization that, in retrospect, we should have heeded as early as the 1990s.
Global warming's repercussions extend well beyond rising ocean levels. The phenomenon has intensified the frequency and severity of tropical storms. Additionally, the augmented CO2 concentrations in our atmosphere have initiated the acidification of oceans, endangering a myriad of marine life.
The alarming rate of global warming was starkly highlighted when an Antarctic research base recorded a temperature of 18.3°C (65°F) in 2020. This marked a notable deviation from the average temperature increase of approximately 3°C (5.4°F) seen over the previous five decades. Scientists widely agree that Antarctica's current glaciation cycle began around 34 million years ago during the Eocene epoch. This onset coincided with a time when atmospheric CO2 levels dropped below 600 ppm. With current levels nearing 414 ppm, and coupled with significant methane emissions, there's mounting concern that we may approach a threshold that could catalyze the melting of the Antarctic ice cap.
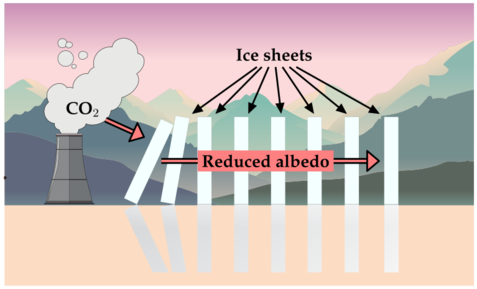
The Albedo Effect
The Earth's climate is intricately linked to the albedo effect, which refers to the reflectivity of a surface to sunlight. Surfaces with a high albedo, such as those covered in ice and snow in regions like Antarctica, Greenland, and the Arctic, reflect a significant portion of incoming sunlight, helping to maintain cooler global temperatures. Conversely, surfaces with lower albedo, like rock, soil, or water, absorb more sunlight. As global temperatures rise and ice and snow melt, these darker surfaces become more prevalent, absorbing more sunlight and further amplifying warming.
This sets off a concerning feedback loop: increasing temperatures lead to more ice melting, revealing darker, heat-absorbing surfaces, which in turn, accelerate warming. This cycle poses severe consequences for the planet's polar regions.
For example, the rapid melting of Antarctica's ice sheets not only destabilizes the region but also contributes significantly to global sea level rise. The Arctic, too, is grappling with rapid sea ice loss, which is transforming its ecosystems and influencing global weather patterns. Similarly, the thawing of Greenland's ice sheet could drastically alter ocean circulation patterns alongside raising sea levels.
The vulnerability of the polar regions to the albedo effect and the potential positive feedback loop it can induce, means that these regions, rich in unique ecosystems, are at considerable risk due to diminishing ice and snow coverage.
Doubling the amount of CO2 in our atmosphere would intensify Earth's warming by adding 3.4 W/M2 of radiative forcing. However, when factoring in the albedo effect, the situation becomes even more critical. As melting progresses, transitioning from reflective ice to heat-absorbing ocean, the Earth could experience an estimated additional 312 W/M2 of energy absorption, far exceeding the impact of CO2 alone.
To put it into perspective: if just 1% of the Earth's reflective ice melts into the ocean, the resultant change in albedo could lead to as much global warming as doubling atmospheric CO2. The mathematical breakdown is as follows: the extra radiative forcing from double the CO2 is 3.4 W/M2, while the heat absorption from a 1% reduction in reflective surfaces is 312 W/M2. A simple division shows that a 1% change in albedo can profoundly influence our climate.
Considering Antarctica, which covers about 3% of the Earth's surface, the potential consequences of its ice melting are monumental. If even a third of its ice were to melt, the resulting drop in albedo could equate to the impact of doubling atmospheric CO2 levels.
It's essential to note that CO2's distribution doesn't uniformly influence the heating effects from decreased albedo. The effects are more pronounced locally. For instance, if one ice sheet collapses, the immediate decrease in albedo could trigger collapses in neighboring ice sheets, creating a cascading effect of melting.
Loss of rainforest
Considered as some of the most biologically abundant and environmentally vital habitats on Earth, rainforests cover merely 6% of our planet's landmass. Astonishingly, it's estimated that a staggering 50-90% of all life forms find their home within these lush environments. Despite their immense importance, these crucial ecosystems are rapidly disappearing, falling victim to human endeavors like farming, logging, and mineral extraction.
From 1970 until now, approximately a fifth of the Brazilian rainforest has been brutally razed, contributing to the global decimation of rainforests. Heartbreakingly, we have lost nearly 64% of these vital ecosystems since the dawn of the industrial age. The primary motivations behind this mass destruction include:
- Expanding Agriculture: The escalating global population has intensified the need for agricultural produces like soybeans, palm oil, and beef. This high demand has consequently accelerated the conversion of lush rainforest territories into expansive farmlands.
- Rampant Logging: The pursuit for valuable hardwoods such as mahogany and teak has led loggers to clear tremendous areas of the forest. This act not only diminishes the forest cover but also lays the groundwork for other destructive activities, including mining.
- Unchecked Mining: The wealth of minerals tucked within the rainforests makes them an alluring target for mining gold, copper, and bauxite. The extraction process, often involving large-scale deforestation and the use of harmful chemicals, inflicts substantial environmental damage.
The devastation of the rainforest has a profound impact on the native communities that have flourished within its confines for thousands of years. This detrimental change not only robs them of their homes and their rich cultural heritage but also threatens their means of survival. Furthermore, the ripple effects of rainforest obliteration extend beyond environmental damage, fueling socio-economic problems such as poverty and sparking social discord.
Loss of fish stocks
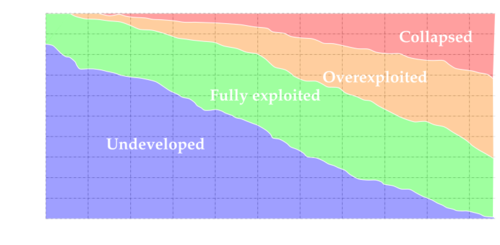
Spanning across approximately 70% of our planet's surface, it's easy to envision the oceans as an inexhaustible pantry. Yet, this perception couldn't be further from the truth. Our insatiable appetite for seafood has led to a rapid and alarming decimation of fish stocks, primarily due to overfishing. Shockingly, today, not a single undeveloped fish stock remains, with a staggering 70% of global fish stocks teetering on the brink of collapse or already being overexploited.
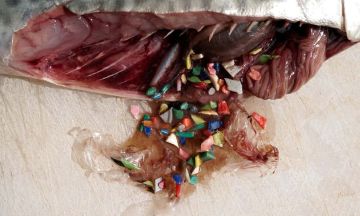
In addition to the ravages of overfishing, pollution is another devastating factor decimating global fish populations. Particularly alarming is the prevalence of plastic waste, a material that can endure for centuries before breaking down. Fish, unable to differentiate between food and these minuscule plastic particles, often end up consuming them. The unfortunate intake of these synthetic materials can result in severe internal harm, bleeding, and even induce untimely death among these aquatic creatures.
Intriguingly, specific variants of plastic harbor detrimental compounds such as diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) and bisphenol-A (BPA), both of which are renowned for their endocrine-disrupting properties that can meddle with hormone activity in humans. In addition to these, other poisonous compounds present in the ocean may cling to fragments of plastic, thus amplifying their capacity for damage. Alarmingly, traces of plastic micro-debris have been unearthed not only in marine creatures but also within agricultural soil and our drinking water supply. The precise extent of health consequences stemming from this pollution remains uncertain. However, preliminary findings suggest the necessity for immediate interventions, one of which could be the promotion of biodegradable plastics in consumer items as a means to mitigate this environmental and health risk.
Pandemic concerns
Human societies are frequently besieged by endemic viruses, including the likes of norovirus, adenovirus, rhinovirus, and influenza, not forgetting the numerous variants of COVID-19. Such viruses are recurrent, persisting and mutating within communities over time. The proliferation of these viruses has been noted, in part due to the leaps and bounds made in virus detection technology. From the advent of tissue cultures in 1948, through to the introduction of monoclonal antibodies in the 1970s, and the implementation of PCR in 1985, our capacity to identify new viruses has been greatly enhanced. Nonetheless, the rise in global interconnectedness and population influx may also be contributing to an actual increase in endemic viruses. This potential surge is a cause for concern, given the potential health implications. For instance, it's well-documented that influenza wreaks havoc on lung epithelial cells, and one can only anticipate similar, if not more severe, damage from the COVID-19 variants. In light of this, our disease control policies should be guided by these realities, with an emphasis on preventive measures to combat this escalating concern.[1]
In our modern healthcare environment, antibiotic and antifungal resistance have swiftly emerged as pressing issues. We are witnessing an alarming evolution of bacteria, which are continually adapting to resist the potency of many prevalent antibiotics. A chilling instance of this escalating problem was highlighted in 2016 when a 70-year-old woman from Washoe County, Reno, was diagnosed with an infection caused by a strain of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae. This particular strain displayed a formidable resistance to all 26 distinct antibiotics it was exposed to for testing at the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This incident serves as a stark reminder of the grave challenges posed by antibiotic resistance.[2]
In the arena of increasing health concerns, the growing threat posed by fungal infections, which have been largely overlooked in medical research, is gaining attention. The medical fraternity has developed and approved fewer drugs to combat fungal infections, in comparison to bacterial ones. This has resulted in a glaring gap in the treatment options available.
One such fungal infection that has been causing a stir in the global medical community is Candida auris. First discovered in a woman's ear in Japan in 2009, this fungus has proliferated across the globe. The troubling aspect of Candida auris lies in its resistance to multiple antifungal medications and its tenacity to thrive on common surfaces such as door handles, textiles, and bed linens for prolonged periods.
Candida auris possesses the ability to inhabit human skin and in extreme cases, it can lead to invasive candidiasis. This condition attacks the bloodstream, central nervous system, and internal organs, boasting mortality rates between 30-60%. These growing health threats emphasize the urgency for comprehensive and anticipatory measures in the formulation of disease control policies.
Arms race concerns
The alarm surrounding the escalation of arms races has been amplified in recent times, primarily because of the advent of sophisticated technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the simplified manufacturing process of bioweapons. The rising trend of nations indulging in competitive military advancements, coupled with the inclusion of AI and the widespread availability of biotechnologies, adds a complicated mix of hurdles and hazards to the arms race scenario. This escalating situation calls for amplified vigilance and enhanced international collaboration.
The accelerated evolution and implementation of AI technologies have dramatically transformed various sectors, including the military. With their unparalleled levels of automation, precision, and rapid decision-making abilities, AI-enabled systems significantly amplify the efficacy and lethal power of weapons systems. However, this surge in AI progression is not without its concerns. As countries battle for technological supremacy, it could inadvertently lead to potentially dangerous consequences, such as the relinquishing of human oversight over autonomous weapons. The prospect of AI-driven weapons independently making critical decisions during a conflict creates ethical and humanitarian dilemmas, and brings with it the threat of unintentional escalation or disastrous incidents.
Moreover, the escalating development and distribution of weapons powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) exacerbate the perils of the arms race. AI technology may fall into the wrong hands, such as those of non-state actors or malevolent groups, who could exploit it for nefarious purposes. These may include launching cyber-attacks, sabotaging vital infrastructure, or instigating unbalanced warfare. The growing dependence on AI within the military arena expands the scope for potential weaknesses and cyber threats. Such vulnerabilities could jeopardize national security, causing an erosion of stability and trust.
Alongside the apprehensions linked to AI, the biotechnology field's progression and accessibility have sparked fears around the creation and utilization of biological weaponry. Biotechnology holds the capacity to equip both governmental and non-governmental entities with the ability to formulate and unleash biological agents, causing catastrophic outcomes. The straightforward accessibility to genetic manipulation tools, coupled with the escalating understanding of pathogens and their control, presents a two-fold predicament. Despite biotechnology promising significant strides in healthcare and scientific exploration, it concurrently harbors substantial biosecurity threats if exploited for malicious intent.
The progression and plausible deployment of bioweapons carry profound implications in terms of ethics, law, and humanity. The deliberate or inadvertent unleashing of an extremely potent disease-causing agent could trigger a disaster of epic proportions, manifesting in extensive sickness, fatalities, and societal upheaval. Compounding this problem, the swift propagation of a genetically modified pathogen could outstrip the capacity of interventions and mitigation strategies, thereby escalating the difficulties encountered by health care systems and emergency response units. It's a fine line to tread, ensuring that biotechnology isn't misused while promoting valuable research and fostering collaborations. This delicate equilibrium demands concerted international efforts, solid regulatory frameworks, and rigorous biosecurity safeguards.
Stock trading concerns
The advent of AI in stock trading underscores a deepening fissure in the bedrock of the contemporary capitalistic system, exposing its unsustainability and the stark inequities it fosters. Entities armed with sophisticated AI platforms are not simply outperforming human traders—they are heralding a seismic shift in the distribution of wealth and power, exacerbating economic disparities. This stark divergence in performance between AI-driven entities and human traders reveals a systemic imbalance, one that threatens to skew market dynamics irreparably.
As these AI technologies continue to advance, the chasm between the technologically empowered and the average market participant widens. The result is an increasingly asymmetrical financial landscape where the upper echelons, equipped with state-of-the-art computational prowess, can manipulate market trends and outcomes to their favor. This disproportionate accumulation of wealth further entrenches the existing hierarchies of power, consolidating financial influence within a narrow segment of society. The monopolization of market advantages by AI-endowed entities reveals the inherent flaws of a capitalistic system that prizes technological dominance over equitable market participation. The speed and efficiency with which these systems operate render human decision-making and traditional trading strategies obsolete, effectively diminishing the agency of the individual investor.
Furthermore, the rise of AI in stock trading amplifies systemic risks. The algorithms that govern these AI systems, operating with opacity and beyond the real-time comprehension of human oversight, have the potential to instigate catastrophic market events. Instances of algorithmic malfunctions have already given us glimpses of this reality, where entire economies could be destabilized due to the unchecked autonomy of AI trading systems. Such technological hegemony within financial markets poses pressing ethical and regulatory dilemmas. The inscrutability of algorithmic trading algorithms challenges the very principles of market transparency and fairness. There is a dire need for robust regulatory frameworks to mitigate against AI-driven market manipulations and to safeguard the integrity of global financial systems.
This unbridled advancement of AI within stock trading serves as a clarion call for transformative economic reforms. As the capitalistic paradigm is pushed to its limits, the imperative for a reimagined system that prioritizes sustainability, equity, and stringent oversight becomes undeniable. Without intervention, the trajectory of current trends points toward an unsustainable future, marked by rampant inequality and the erosion of democratic economic participation. The time is now for policymakers, regulators, and civil society to coalesce around a vision for a more just and stable economic order—one that can withstand the tides of technological upheaval.
Government Interventions
While individual and organizational acts of charity are admirable, they might not always be adequate to meet the vast needs of society. Depending solely on voluntary contributions can result in unpredictability, leading to feelings of insecurity and vulnerability. This unstable dynamic might restrict our sense of freedom, knowing that aid might be inconsistent.
Conversely, state-administered welfare programs offer a structured and reliable support system. These government initiatives ensure that citizens have access to essential services like food and healthcare, enhancing their sense of security. State-led welfare removes the inconsistencies of charitable acts, promising steady and uniform assistance.
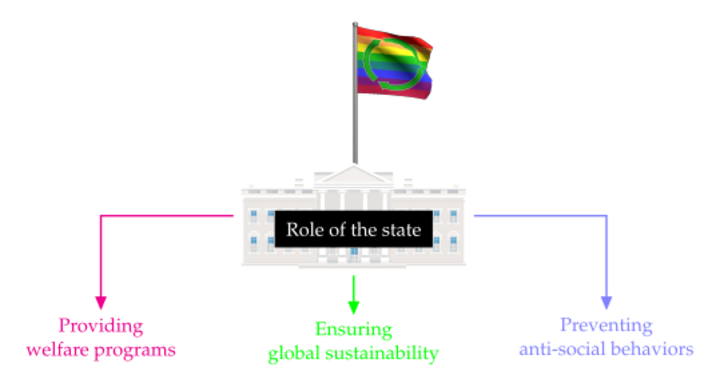
Beyond welfare, governments play a vital role in curbing harmful societal behaviors and championing global sustainability. They bear the responsibility to introduce and enforce regulations that deter negative actions and promote communal prosperity. Additionally, these institutions are central in advancing environmental policies, contributing significantly to global efforts to preserve our planet.
It's essential for governments to effectively execute their societal responsibilities. When shortcomings arise, they must be addressed promptly and comprehensively. While holding the government accountable is essential, recognizing its integral role in addressing the complex challenges the world faces today is just as crucial.
Governments symbolize the collective will of their citizens, tasked with their overall welfare. An essential aspect of this role involves championing global sustainability, understanding that the well-being of its populace is intertwined with the health of the Earth.
Therefore, governments are duty-bound to take bold steps on environmental issues, including reducing carbon emissions, conserving biodiversity, and ensuring the sustainable utilization of natural resources.
Ensuring welfare remains a primary responsibility of the state, guaranteeing access to essentials like food, housing, and medical care for all. Furthermore, the state should ensure that educational and job opportunities are accessible to everyone. A sound welfare structure is a state's primary defense against poverty and disparity, creating a stable and thriving society.
The state is also pivotal in countering disruptive behaviors, encompassing criminal activities and extremist threats. It involves rigorous law enforcement and resource allocation to address root causes. Additionally, it's the state's duty to foster unity and inclusiveness, actively combating discrimination and ensuring every citizen feels valued and engaged.
Choosing the right welfare programs and preventive measures transcends political leanings, sparking profound philosophical discussions. Encouraging honest and constructive dialogues allows diverse perspectives to enrich the discourse, leading to holistic solutions benefiting the community.
However, intellectual progress can stagnate due to political tribalism and the inclination towards 'in-group' vs. 'out-group' dynamics. These patterns prevent open-minded exploration and hinder collaborative discussions.
To counter such divisive tendencies, fostering a culture that values intellectual curiosity and inclusivity is paramount. Prioritizing dialogue and cooperation over dissent and division can pave the way for a more enlightened, cohesive society. Embracing unity and focusing on shared objectives can propel us towards ensuring the betterment of all.
Wealth redistribution policies
Wealth, when viewed as a communal responsibility, isn't merely an individual's asset but a societal duty. This perspective highlights how one person's wealth accumulation impacts society at large. When someone amasses significant wealth, it suggests a substantial societal obligation to them. Such individuals can command vast resources, goods, and services, often at the detriment of those less privileged.
Concentration of wealth in the hands of a few can have adverse societal effects. These economic imbalances can hinder the financial growth of the majority by limiting their access to resources and opportunities. Such wealth disparity can destabilize social and economic foundations, and in extreme situations, incite political unrest.
Furthermore, those with vast fortunes often have disproportionate influence over political and economic systems. Such influence can result in policies that protect their interests, potentially undermining accountability, transparency, and representation for the broader community.
Prioritizing rapid economic growth can lead to short-sighted decisions that prioritize immediate gains over long-term sustainability. This approach risks depleting natural resources and causing environmental degradation, which poses threats to both the planet and future generations.
Reflecting on these insights, we're prompted to reevaluate our current economic systems and the role of wealth within society. Solutions might include promoting equitable wealth distribution, championing sustainable growth, and developing new economic frameworks that prioritize societal well-being over individual prosperity.
Imagine implementing a Universal Basic Income (UBI) to guarantee basic sustenance for all, irrespective of employment status. Recognizing various forms of value, such as time, community resources, and environmental conservation, can promote a balanced economic structure.
UBI proposes regular, unconditional financial assistance to everyone, ensuring coverage for essential needs. With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation replacing human jobs, UBI becomes even more crucial. It could provide financial stability, allowing individuals to pursue education, start businesses, or address familial needs without financial anxiety.
As automation advances, ideas like providing free access to food and other basic rights alongside UBI become feasible. Innovative food production methods might enable free food distribution to everyone, ensuring nutrition, better public health, and reduced socio-economic inequalities.
In a society powered by automation, universal access to basic rights like health care, education, and housing becomes achievable. Such an approach ensures that everyone, regardless of background, can lead a fulfilling life.
Welfare policies
Food as a human right
Historically, a significant part of the human population was deeply entrenched in agricultural activities, with individual farmers frequently battling to cultivate sufficient food for their own sustenance. Yet, the landscape of this dynamic has been radically transformed by the emergence of innovative technologies and advanced farming methods.
The advent of the tractor in the mid-19th century marked a significant turning point in the field of agriculture, drastically improving labor efficiency and output. This revolutionary technology empowered a single farmer to nourish approximately ten individuals, a feat previously unthinkable. Consequently, a smaller number of farmers could generate a greater food supply, allowing others to explore different career paths.
The journey of progress has been unceasing. Over time, agriculture has consistently evolved, embracing a myriad of innovative technologies and methodologies including mechanization, irrigation, as well as the application of fertilizers and pesticides. These forward strides have heralded significant leaps in crop productivity and have consequently reduced the dependence on human labour in agricultural processes.
The outcomes of the agricultural revolution have led to a considerable decline in the proportion of people involved in farming activities. In contrast, there has been an impressive surge in agricultural productivity. This transformation has deeply impacted society, resulting in a decrease in food expenses and an enhancement in the standard of living for a large section of the population. Furthermore, it has spurred the phenomenon of urbanization, as individuals migrate from countryside settings to bustling urban hubs in pursuit of employment opportunities.
The advent of AI and automation has the power to revolutionize agriculture, making it more sustainable and efficient. Techniques such as precision farming leverage the capabilities of drones and other self-controlled vehicles for tasks like planting and harvesting. This not only minimizes human effort but also economizes energy usage. Additionally, the power of AI extends to the continuous surveillance of crop health and soil status. This allows farmers to fine-tune the conditions for crop growth, thereby enhancing yield potential.
Advancements in agricultural technology could hold profound implications for worldwide food security. As the global populace is anticipated to near 10 billion by 2050, the demand for sustenance is set to rise accordingly. Traditional farming techniques, however, often lack the requisite efficiency and sustainability, thereby raising concerns about potential food scarcity and skyrocketing costs. The integration of AI and automation into farming practices could potentially boost crop production and reduce expenses. This could pave the way to adequately feeding the global population, regardless of their financial status or geographic locale.
Furthermore, artificial intelligence (AI) and automation hold immense potential to tackle pressing environmental issues like deforestation, water scarcity, and greenhouse gas emissions. By promoting efficient and eco-friendly farming techniques, we can reduce the reliance on land and water resources for food production, as well as minimize the employment of damaging chemicals and pesticides.
The extraordinary advancements in agricultural productivity suggest that it might be the right moment to regard access to food as an essential human right. Should everyone dedicate merely a couple of hours weekly to support high-efficiency farming methods, it could potentially be enough to nourish the entire world's populace.
The proposition for universal access to food can be strongly rooted in the advancement of contemporary automated farming technologies. Breakthroughs in the form of precision farming and the integration of drones and robots for crop cultivation and harvesting have considerably boosted agricultural productivity. These technological leaps don't just cut costs; they also improve food accessibility for all. Additionally, the application of artificial intelligence in agriculture has the potential to maximize crop yield while minimizing environmental damage by reducing reliance on resources such as water, energy, and pesticides.
Through the guarantee of universal food access, we have the potential to make substantial progress in alleviating poverty. This not only enhances overall health and well-being but also promotes the creation of a society that is more sustainable and fair.
The Fundamental Right to Shelter
Offering homes to the homeless is not merely an act of compassion; it's an essential step towards individual and collective progress. The detrimental effects of homelessness weigh heavily on the mental, physical, and emotional well-being of those ensnared in its grasp. Addressing this challenge is pivotal in fostering an equitable and harmonious society.
Central to this discussion is the understanding that shelter is a foundational human necessity. Viewing housing as an intrinsic human right underscores the commitment to ensuring every individual has a safe and stable environment. Without a home, individuals face a myriad of vulnerabilities ranging from exposure to extreme weather conditions and potential violence to heightened risks of communicable diseases. By ensuring housing for the homeless, we not only counter these hazards but also elevate their quality of life.
Furthermore, proactively addressing homelessness by furnishing proper housing can alleviate the economic pressures on the broader community. Homeless individuals often lean heavily on emergency services, from healthcare facilities to law enforcement. This dependency results in substantial costs borne by the community. However, providing consistent housing curtails this reliance, transforming the approach to homelessness from a reactive expense to a proactive investment in societal health.
Moreover, ensuring housing acts as a potent remedy to disrupt the vicious cycle of poverty and displacement. Homelessness is often the outcome of intertwined challenges like poverty, unemployment, and the scarcity of affordable housing. Addressing homelessness head-on can mitigate these root causes, thereby reducing the recurrence of destitution and displacement, enhancing the economic prospects for the affected, and uplifting the community's general welfare.
In summation, it's an ethical imperative to provide shelter to the homeless. The quandary of homelessness isn't merely a societal dilemma; it's a testament to our collective conscience. Assurances of secure housing for every individual mirror a community's unwavering commitment to justice, inclusivity, and the holistic growth of all its members.
Universal Health Care: A Fundamental Right
Universal health care, encompassing free medical care for all, is more than just a benevolent ideal—it's a critical cornerstone for a just and equitable society. Recognizing health care as an inherent human right brings a plethora of benefits, both on an individual and societal level, solidifying its position as an essential component for communal well-being.
At its core, universal health care aims to ensure that every individual, irrespective of their economic background, receives essential medical treatments and preventive services. This principle holds immense significance for those with chronic conditions requiring continuous care and for those who might otherwise be sidelined due to lack of insurance. By championing universal access, we are actively contributing to the holistic health and vitality of our entire community.
Furthermore, universal health care serves as a powerful tool in addressing and diminishing health disparities. In the current landscape, those without comprehensive insurance often grapple with adverse health outcomes—ranging from chronic diseases to increased mortality rates. By guaranteeing healthcare access to all, we can mitigate these discrepancies. This initiative not only fosters health equity but also ensures that everyone, regardless of their financial standing, can enjoy optimal health outcomes.
From an economic perspective, universal health care presents considerable fiscal advantages. By emphasizing preventive care and offering a wide spectrum of medical services, we can significantly reduce the onset of severe health issues that often lead to costly medical procedures or prolonged hospital stays. This proactive approach not only ensures better health for individuals but also translates into substantial savings in overall healthcare expenditures.
In essence, advocating for universal health care is both a moral and societal imperative. Every individual deserves the right to quality health care, devoid of financial constraints. Embracing this ethos is a reflection of our commitment to justice, inclusivity, and the shared prosperity of all citizens.
Environmental policies
The impact we have on our environment, as a result of our activities, can be measured by our environmental footprint. This footprint paints a comprehensive picture of how we use resources, generate waste, and contribute to pollution. A widely accepted approach to ascertain this influence is through the calculation of an ecological footprint. This approach determines the required land and water resources needed to sustain the consumption habits and waste management of an individual, a community, or even an entire nation.
The environmental impact of a person's lifestyle is shaped by a range of personal choices, spanning from their diet to travel habits, energy consumption, and buying behaviors. For example, a diet heavy in meat and dairy tends to amplify one's environmental footprint. This is because the production and transportation of these animal-derived products are resource-intensive. Similarly, relying on a gas-guzzling vehicle for transportation inflates one's footprint when compared to commuting via public transit or driving fuel-efficient vehicles.
On a national scale, various elements such as the size of the population, the degree of industrialization, and the stage of economic growth can influence a country's environmental impact. It is often observed that developed nations leave a larger ecological imprint, primarily due to their increased resource use and greater generation of waste.
Our planet is under immense strain due to the substantial environmental footprint we leave behind, leading to detrimental effects such as deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and pollution of our air and water bodies. These issues not only disrupt our ecosystem but also create a scarcity of resources, potentially fueling conflicts. Therefore, to ensure our environment's longevity and pave the way for a sustainable future, it's paramount that we endeavor to minimize our environmental footprint.
Coal is the primary culprit in CO2 emissions, closely trailed by oil, natural gas, and cement manufacturing. Our energy consumption today is heavily reliant on fossil fuels, contributing to approximately 80% of our total energy use. With this escalating reliance comes an increased susceptibility to the impending exhaustion of these crucial resources. Moreover, intensifying our rate of fossil fuel extraction and consumption only magnifies this susceptibility.
Comprehending the carbon impact of diverse industries forms the backbone of devising successful measures to curtail greenhouse gas releases and combat global warming. Be aware, these proportions represent global medians and can fluctuate markedly across different countries and regions, contingent on their energy provisions and industrial methodologies.
- Power & Thermal Energy Generation (25%): This sector stands as the most substantial contributor to the world's total greenhouse gas emissions. The primary cause is the combustion of coal, natural gas, and oil for heat and electricity. The process not only generates emissions from burning fossil fuels but also from the 'fugitive emissions' that occur during their extraction, processing, and distribution.
- Agriculture & Land Use (24%): This category encompasses agricultural practices and land use changes, including deforestation, which significantly contribute to global warming. The emissions originate from several sources: crop and livestock cultivation that produce methane and nitrous oxide, residue burning from farming activities, and the conversion of forests into agricultural land causing carbon dioxide emissions.
- Manufacturing & Building Industry (21%): This sector's emissions are due to chemical reactions needed to transform raw materials into finished products, and the fossil fuels burned to provide heat for these processes. The construction industry plays a part too, with the manufacturing of cement, steel, and other construction materials contributing to emissions.
- Transportation (14%): All forms of transport such as personal vehicles, trucks, maritime vessels, aircraft, and rail systems fall into this category. The predominant source of these emissions is the combustion of fossil fuels, specifically petroleum-based fuels like gasoline and diesel, used in over 90% of transportation means.
- Miscellaneous Energy Sources (10%): This category covers emissions from various aspects of fuel production like extraction, refining, processing, and delivery. It also includes emissions from burning fuels for energy in sectors outside those listed separately.
- Other Industrial Activities (10%): This section pertains to emissions resulting from industrial processes not classified under the energy sector. These emissions stem from the production of a wide range of goods and services, such as cement, chemicals, metals, and mineral extraction.
- Building Infrastructure (6%): Both direct and indirect emissions are associated with buildings. Direct emissions come from fossil fuel usage for heating and cooling purposes, while indirect emissions arise from electricity use, which is frequently powered by fossil fuels. Implementing energy-saving measures and using renewable energy sources can help mitigate these emissions.
Sustainable Protein: The Power of Legumes
The agricultural sector dominates our land usage and is a significant consumer of our freshwater resources. In fact, over 70% of global freshwater is dedicated to agriculture, a figure that starkly contrasts with the mere 10% allocated for domestic use. This significant disparity implies that household water conservation measures, such as shorter showers, might only have a minimal effect on global freshwater conservation.[3] [4]
Interestingly, while grains make up the bulk of human caloric intake, a large portion of it is directed towards feeding livestock. However, the conversion of grain into meat is inefficient, with a lot of energy lost through animal metabolism.
As the global population ages and continues to grow, dietary choices play a pivotal role in resource management.
Legumes, which include beans, lentils, and peas, are emerging as a sustainable protein alternative to traditional animal-based proteins. The environmental toll of animal agriculture is profound, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, habitat destruction, and water pollution. The industry's resource demands are vast, requiring significant amounts of feed, water, and land, while also generating considerable waste. Livestock, notably, are major emitters of methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Conversely, legumes offer a green and sustainable protein source. They are resource-efficient, needing far less water and land compared to many traditional crops. A unique attribute of legumes is their nitrogen-fixing capability, which reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers. Their drought-resistance and adaptability to diverse environments, even in nutrient-poor soils and semi-arid regions, emphasize their potential as an eco-friendly food source.
While it's crucial to acknowledge that protein production's environmental footprint varies considerably, it's equally important to recognize that it's largely contingent on factors such as production techniques, geographic location, crop rotation strategies, and the employment of pesticides and fertilizers. Take soybeans, for instance. These legumes can have a considerable environmental toll, primarily due to the extensive monocultures and the correlating deforestation measures.
Renewable Power: Wind and Sun
Tapping into the boundless might of wind and sunlight emerges as a pivotal strategy in addressing the world's growing energy needs, offering an array of ecological, financial, and societal benefits.
The ceaseless force of the wind can be harnessed to convert its kinetic energy into usable electricity. This sustainable mode of power generation emits no harmful gases or residues, making it a champion for environmental conservation. Transitioning to wind energy diminishes our dependence on non-renewable fuels, preserving our planet's ecosystems for future generations. Notably, the footprint of wind turbines on land is minimal, allowing adjacent land to be used for endeavors like agriculture. This coexistence not only offers supplementary income sources but also fosters development in less urbanized regions.
Economically, the realm of wind energy is a vibrant hub for job opportunities. It spans roles in manufacturing, installation, upkeep, and management. Such roles catalyze economic growth and open doors for local employment. Additionally, the cost trajectory of wind power has been consistently downward, making it an increasingly affordable choice for electricity generation.
Both wind and solar energy are characterized by their abundance, renewability, and eco-friendliness, marking them as cornerstones of a sustainable energy future. Solar panels exemplify this potential by converting the abundant sunlight, available almost everywhere and endless on a human timescale, into direct electrical energy.
Solar setups, especially apt for regions with space constraints, can be integrated seamlessly onto rooftops or other underused spaces. Their modular nature allows them to be tailored to diverse energy needs. Whether it's charging a handheld device or energizing an entire neighborhood, solar solutions cater to a wide spectrum of demands.
Moreover, solar systems contribute to energy resilience and autonomy. Distributing energy production across individual solar installations reduces reliance on centralized power infrastructures, ensuring a more resilient energy supply that can withstand potential disruptions.
Together, wind and solar energies stand as formidable forces in the quest to counteract climate change and transition to a sustainable energy paradigm. Their multifaceted benefits illuminate a path of hope, steering society towards an environmentally conscious future.
Metro and train
Urban rail systems, including metros and trains, offer a myriad of advantages for transportation. Foremost among these is their unparalleled efficiency. Designed to transport large numbers of passengers quickly, they alleviate congestion on roads and highways, offering a faster, smoother journey for many.
Furthermore, metros and trains are more environmentally friendly than many transportation alternatives. They produce fewer emissions and consume less energy on a per-passenger basis, making them a preferred choice for a sustainable future.
From an economic standpoint, these rail systems are often more cost-effective. The ability to accommodate a large number of passengers simultaneously means they can offer a budget-friendly alternative to the costs involved in owning, operating, and maintaining a private vehicle.
Beyond their core function, metros and trains provide a range of amenities that enhance the commuter experience. With features like air conditioning, Wi-Fi access, and sometimes even catering services, they ensure that passengers travel in comfort and convenience.
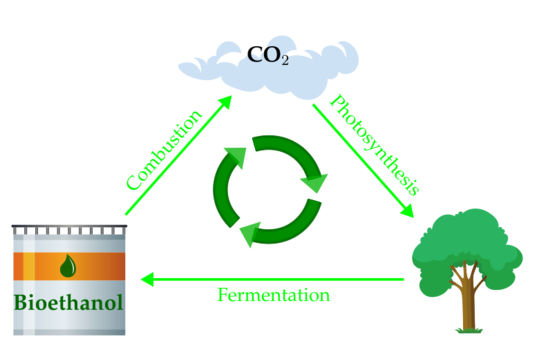
Bioethanol Fuel Cells
The benefits of bioethanol fuel cells are numerous, and paramount among them is their impressive efficiency. In energy parlance, 'efficiency' denotes the percentage of energy in the fuel that can be harnessed as usable electricity. Contrasting gasoline engines, bioethanol fuel cells can convert as much as 60% of the energy encapsulated in bioethanol into electricity you can actually use. The secret to this extraordinary efficiency lies in the fuel cell's inherent design. The electrochemical reactions that take place within these cells are fundamentally designed to be more efficient than their internal combustion counterparts, thus making bioethanol fuel cells a far more effective energy converter.
In addition, bioethanol fuel cells present a notable advantage in terms of CO2 emissions, which are substantially less than those generated by traditional combustion engines. The CO2 output originates from the burning of bioethanol within the fuel cell itself. Interestingly, if this bioethanol is sourced from biomass materials - such as plants that naturally absorb CO2 - the entire process could potentially reach a state of carbon neutrality. The reason being, the volume of CO2 discharged by the fuel cell would be equal to the amount of CO2 that the plants had previously absorbed throughout their lifecycle.
Bioethanol fuel cells emerge as a superior choice when compared to other energy alternatives like hydrogen fuel cells, lithium batteries, or gasoline engines. One of their primary advantages lies in their exceptional energy density. Bioethanol has the capability to store more energy in a given volume than the chemical components used in lithium batteries. This superior energy density allows the same energy quantities to be stored in a more compact space. This is a considerable advantage, especially in applications such as portable power generation and transportation, where being lightweight and compact are key factors.
Bioethanol fuel cells offer enhanced longevity, a feature that sets them apart. Unlike their lithium battery counterparts, which are restricted by a finite number of charging and discharging cycles, fuel cells can potentially endure for a staggering tens of thousands of hours, depending on their design and how they're used. Furthermore, these cells can be expertly designed to be more compact and lightweight than traditional combustion engines, a characteristic that amplifies their usefulness for specific applications.
The use of bioethanol fuel cells offers the advantage of generating electricity at a constant voltage, providing greater stability than their lithium battery counterparts. This stability is key for electronic devices that demand a consistent voltage to operate effectively. Furthermore, bioethanol's liquid form simplifies its transportation and storage, unlike lithium batteries that necessitate specific storage conditions and handling protocols.
When stacked up against hydrogen fuel cells, bioethanol fuel cells have a clear edge. A striking advantage is how bioethanol, being a liquid fuel, simplifies both storage and transportation. On the other hand, hydrogen gas needs high-pressure tanks or cryogenic storage, factors that contribute to its complexity and inflate its cost. Bioethanol outshines hydrogen in another critical aspect - energy density. With a higher energy density and lower cost, bioethanol is poised to be a more appealing choice for large-scale implementations. Moreover, bioethanol fuel cells present a reduced explosion risk compared to their hydrogen counterparts. The extreme flammability of hydrogen can trigger easy ignitions and potential explosions if not handled with utmost caution.
Fuel Pump Systems: Preventing Misfueling
Every year, engines worth billions of dollars suffer damage due to a common yet preventable issue: misfueling. This occurs particularly when gasoline is mistakenly filled into diesel engines. As we consider the transition from traditional fuels like gasoline and diesel to biofuels such as bioethanol and biodiesel, we must recognize that similar challenges are likely to persist. Although biofuels are more sustainable, they introduce new complexities due to their distinct properties and engine compatibilities. Misfueling incidents could become more frequent, with engines designed for one type of biofuel being erroneously filled with another. Furthermore, biofuels necessitate specific production, transportation, and storage facilities, complicating the fuel supply chain. Transitioning to biofuels would require significant modifications to existing fuel distribution infrastructures, including pumps and storage tanks. In the absence of clear regulatory guidance and industry-wide standards, the risk of misfueling and its associated costs could remain a significant barrier. This hurdle could hinder the widespread adoption and appropriate infrastructure development for biofuels. One potential solution is the implementation of standardized fuel pumps – round for bioethanol and rectangular for biodiesel vehicles – to physically prevent misfueling.
This issue of overlooking simple solutions due to dispersed costs is not unique to the fuel industry. It is a phenomenon observed across various sectors, from healthcare to urban planning. Often, potential improvements are not realized because the costs and inconveniences are distributed among many individuals or over extended periods. This leads to a lack of urgency in any single party to initiate change, despite the collective burden borne by society.
Geothermal Heating
Geothermal heating, often known as ground heating, is a cutting-edge approach that leverages the Earth's stable temperatures to provide consistent warmth to homes and commercial establishments. This system is grounded in the principle of tapping into the planet's innate heat, presenting numerous benefits for both homeowners and commercial property owners.
Foremost among its advantages is energy efficiency. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely heavily on fossil fuels, geothermal heating capitalizes on the Earth's natural, renewable energy. This results in impressive energy conservation, with potential reductions in energy consumption reaching up to 70% compared to conventional methods.
From an economic standpoint, geothermal heating offers substantial cost savings over time. The durability and efficiency of these systems mean that users can expect reduced utility bills. Additionally, due to their robust design, maintenance and repair costs are significantly lowered.
Environmentally, geothermal heating is a standout. Drawing from the Earth's renewable heat means we can decrease our dependence on finite resources and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. This makes geothermal heating a prime option for those aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
Beyond its heating capabilities, geothermal systems also contribute to healthier living spaces. By forgoing the need for air ducts, which can accumulate dust, mold, and other allergens, indoor air quality is markedly improved. This is a boon for reducing health risks associated with indoor air contaminants.
Lastly, the reliability of geothermal heating cannot be overstated. The Earth's temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year, enabling these systems to provide consistent warmth regardless of external weather conditions. This ensures not only the comfort of indoor spaces but also positions geothermal heating as a top choice for those seeking a reliable and pleasant indoor environment.
Geothermal City Heating
To further capitalize on the potential of geothermal heating, a city can embark on a more ambitious project: developing a comprehensive geothermal heating network to service the entire urban area. This would involve drilling deeper into the Earth's crust to access even higher temperatures, which could then be harnessed to provide heat on a much larger scale.
Such a city-wide geothermal heating system would require significant initial investment in infrastructure. This includes the installation of an extensive network of underground pipes and heat exchangers, as well as the construction of central heating facilities. However, the long-term benefits would be substantial. Not only would this reduce the city's overall energy consumption and carbon footprint, but it would also lead to economies of scale, potentially making heating costs for end-users even more affordable.
The implementation of a city-wide geothermal system also offers an opportunity for urban renewal and sustainable development. As part of the installation process, cities could revitalize aging infrastructures, incorporating green spaces and sustainable design principles. This would not only improve the aesthetics and functionality of urban areas but also enhance the quality of life for residents.
Moreover, such a system could be integrated with other renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, to create a hybrid system that further increases efficiency and reliability. This integration could be particularly effective in regions with fluctuating renewable energy outputs, as the consistent heat supply from geothermal sources would balance the intermittent nature of other renewables.
In terms of community engagement, the development of a city-wide geothermal heating system could foster a sense of communal responsibility and pride. Educational programs and public awareness campaigns could highlight the benefits of renewable energy and encourage sustainable practices among citizens.
Finally, on a larger scale, a city with a comprehensive geothermal heating network would serve as a model for sustainable urban living. It could inspire other cities globally to adopt similar systems, thereby contributing to the broader fight against climate change and promoting a more sustainable future for all.
Sustainable Water Management
Embracing sustainable water and sewage management practices offers indispensable benefits for communities, the environment, and the broader economy. Central to this approach are two pivotal components: local wastewater recycling and the establishment of advanced water distribution networks.
Local wastewater or sewage recycling presents a multitude of advantages. Foremost among these is the assurance of a consistent supply of treated, safe water. Such recycled water can be repurposed for various applications, ranging from agricultural irrigation to industrial processes, and under stringent conditions, even for direct consumption. This system reduces dependency on dwindling natural water sources such as rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers.
From an environmental perspective, wastewater recycling promotes a sustainable waste management approach. By treating and reusing sewage, we substantially reduce waste output and its associated environmental impacts. This includes minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, preventing pollutants from contaminating our ground and surface waters, and addressing nuisances like odors and other disturbances.
Economically, the practice of recycling wastewater eliminates the need for constructing new sewage treatment facilities. This translates to considerable cost savings, positioning wastewater recycling as a cost-effective solution for communities.
Complementing wastewater recycling, efficient water distribution systems offer their own set of benefits. Primarily, they ensure a steady provision of clean and potable drinking water, which is vital in regions facing water scarcity or contamination. By facilitating access to uncontaminated water, these systems dramatically decrease the risk of waterborne diseases, bolster hygiene, and uplift the overall health of the community.
Well-designed water distribution infrastructures, particularly pipe networks, are vital for conserving water. They minimize losses from leaks and evaporation, especially crucial in areas prone to drought or with limited water reserves. By mitigating water wastage, these systems ensure that communities have sufficient water for essential activities.
Zooming out to a broader perspective, the importance of sustainable water management, combining both wastewater recycling and efficient pipe networks, is profound. Together, they reduce the demand for freshwater from natural sources and minimize wastewater discharge into the environment. This not only conserves our vital water resources but also reduces environmental stress. Additionally, these practices enhance the health of local water ecosystems.
In essence, the merger of localized sewage treatment and advanced water distribution infrastructures offers a comprehensive, sustainable water management solution. This strategy prioritizes public health and plays an instrumental role in environmental conservation.
Avoiding catastrophe
Given that our consumption rate is roughly 50 percent higher than what our Earth can sustainably replenish, it's paramount that we initiate concrete measures to stave off the impending environmental catastrophe.
A crucial tactic in averting impending disaster lies in the modification of our dietary habits to lessen our agricultural impact. The resource-heavy process of livestock farming can be substantially mitigated by shifting from a beef-heavy diet to one that's more vegetable-based. Additionally, the implementation of avant-garde agricultural practices like farming powered by artificial intelligence and the cultivation of plants in water (hydroponics) can boost agricultural productivity exponentially.
Transitioning to green energy alternatives is another crucial strategy to avoid catastrophic consequences. Encouraging the widespread usage of solar panels and wind turbines could significantly diminish our dependency on electricity produced from fossil fuels such as coal. Moreover, the incorporation of ground heating systems in residential structures can augment this initiative by decreasing the overall demand for electricity.
Shifting our transportation paradigm to incorporate methanol fuel cells in cars could be a pivotal move in anticipation of dwindling oil reserves. As a renewable energy alternative, these cells not only serve to replenish our energy needs, but also present a cleaner alternative. Unlike their fossil fuel counterparts, they don't exacerbate the carbon dioxide levels in our atmosphere.
We can also mitigate the damaging impact of pollution by adopting the use of more biodegradable plastic alternatives. This will help to curtail the piling up of non-degradable plastics that continue to plague our oceans and natural habitats.
In conclusion, the initiation of worldwide rules safeguarding our rainforests can serve as an essential step towards conserving these crucial ecosystems. This collective action could substantially alter our course, steering us clear of an impending environmental disaster.
Let's ponder a scenario: our ongoing trajectory, marked by rampant resource exploitation and continually escalating CO2 levels, could potentially bring about dire outcomes. One could theorize that environmental devastation could catalyze a human catastrophe of up to half a billion fatalities, inundation of coastal metropolises, and large-scale crises related to starvation and mass displacement. Furthermore, we could also experience a distressing decline in biodiversity.
Imagine instead a different course of action. What if we took bold, proactive measures starting today? What if we substantially minimized our agricultural impact and slashed our CO2 emissions? Such actions could dramatically reshape our future landscape. The projected 500 million lives at risk might instead be reduced to 50 million, a devastating yet significantly lesser figure. More than that, the majority of our planet's diverse life forms could be preserved. While these scenarios are purely speculative, with the actual figures possibly being much higher or lower, they underscore the critical nature of the situation we are in and the immediacy of our response. The obstacle we face is monumental, but equally substantial is the potential for transformation. It's imperative that we direct our collective efforts towards addressing this global crisis and pledge to steer the world towards a sustainable future.
Education policies
Education is the cornerstone of societal progress, playing a crucial role in nurturing individual development and moulding the future of our shared world. Therefore, crafting impactful education policies requires a delicate balancing act. This includes encouraging self-driven learning, imparting global human rights principles, preserving cultural sovereignty, and leveraging artificial intelligence's potential to create an adaptable learning environment.
Education is not merely about information acquisition; it's about sparking a deep-seated desire to learn for the sheer pleasure it brings and the personal growth it facilitates. This innate drive is known as intrinsic motivation, and it can transform education from a chore into a passion. Educational policies should strive to cultivate and nourish this inner flame, with the goal of creating lifelong learners who actively pursue knowledge, comprehend their own learning pathways, and flexibly adjust to ever-changing scenarios. This can be realized through the implementation of teaching strategies that center around the student, the promotion of analytical thinking, the stimulation of intellectual curiosity, and the provision of opportunities that allow students to take charge of their own learning journey.
Education should serve as a conduit for imparting values of universal human rights. It should create a sanctuary where principles of justice, equity, and fairness are not just preached, but deeply instilled in the learners, fostering a deep-seated respect for these fundamental tenets. Educational policies should underline the significance of human rights education. They should illuminate students about their entitlements and obligations, the richness of diversity, and the crucial role of social justice. By doing so, we are not merely crafting an enlightened populace but also nurturing a future generation committed to upholding the dignity and value of every individual.
In conjunction, it is essential that education policies uphold cultural independence. Given the multifaceted nature of our global community, it's crucial to cultivate an educational environment that recognizes, values, and integrates a variety of cultures. We must strive to create an education system that is globally conscious yet locally adaptable, allowing individual regions or communities the flexibility to weave their distinct cultural heritage and history into their educational structures.
As we venture further into the digital era, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) within our education system presents vastly promising opportunities. With the power to completely transform the landscape of education, AI holds great potential in tailoring education to individual needs, offering immediate feedback, and aiding educators in pinpointing and tackling learning deficiencies more effectively. AI can usher in a new era of adaptive learning landscapes, fine-tuned to cater to each student's unique learning style, thereby boosting student engagement and augmenting academic achievements. Hence, it's crucial for education policies to advocate for the mindful employment of AI in our classrooms, ensuring that everyone has fair access to this innovative technology in education. However, it's also equally important to address the potential issues surrounding privacy and data security that may arise.
To sum it up, the formulation of impactful educational policies necessitates a judicious equilibrium of multiple factors. This includes nurturing inherent motivation in students, instilling principles that resonate universally, preserving cultural uniqueness, and leveraging the revolutionary capabilities of Artificial Intelligence. This holistic approach allows us to progress towards an educational framework that is capable of equipping learners to effectively navigate the future's complexities and seize its opportunities.
Research policies
The idea of an AI-powered database for scientific research is intriguing and has the potential to address several of the issues currently plaguing scientific publishing. Let's explore how such a system could function and its potential benefits:
- Repository for All Research: This database would serve as a central hub for all scientific research, including both positive and negative results. By capturing a comprehensive range of data, it would help mitigate the publication bias towards positive findings.
- Registration and Verification of Researchers: By requiring scientists to register with institutional credentials, the system could ensure that only legitimate researchers are contributing. This step would help maintain the integrity of the data in the database.
- Tracking Replications and Verifications: One of the key features would be the ability to track who has replicated a study and their findings. This would provide valuable insights into the reliability and reproducibility of research. It could highlight studies that have been successfully replicated multiple times, as well as those that have failed replication attempts, offering a more nuanced view of the research landscape.
- Standardized Research Formats: Implementing standardized formats for submitting research could streamline the process and make it easier to compare and contrast studies. This could include standardized methodologies, data reporting formats, and statistical analyses, which would facilitate peer review and meta-analyses.
- AI-Powered Analysis and Categorization: Utilizing AI for analysis could help in categorizing research, identifying trends, and even flagging potential errors or inconsistencies in data. AI could also assist in meta-analyses by quickly synthesizing data from multiple studies.
- Open Access and Transparency: Such a database would ideally be open access, allowing free availability of research findings. This transparency would democratize access to scientific information, enabling more widespread scrutiny and discussion.
- Encouraging Collaboration and Reducing Duplication: By having a comprehensive view of ongoing and completed research, scientists could identify gaps in knowledge more easily, avoid duplicating efforts, and find potential collaborators.
This AI database concept represents a significant shift from the current publishing model and could revolutionize how scientific research is conducted, shared, and validated. However, it would require substantial cooperation across the scientific community, significant funding, and rigorous standards to ensure its success and sustainability.
Nutritional research
In numerous countries around the world, the prevalent use of credit cards for food purchases has streamlined the collection of consumer buying data. Grocery stores and supermarkets routinely track and analyze these transactions, amassing detailed statistics on the purchasing habits of diverse demographics. This wealth of data, readily captured through digital payment methods, offers a treasure trove of information for researchers. Utilizing this existing dataset for nutritional and consumption pattern research presents a minimal challenge, as it bypasses the traditional hurdles of data collection and entry. The digital footprint left by credit card transactions at grocery stores can be anonymized and aggregated to provide valuable insights into dietary trends, preferences, and behaviors at a population level. This method not only enhances the efficiency of research but also improves its accuracy by leveraging real-world purchasing data, making significant contributions to public health studies and policy-making.
Contrary to the belief that we consume everything we purchase, a significant portion of our food purchases may not be consumed directly by us. Some of it could be thrown away, while other items might be shared with friends or family. Despite this, there's a notable relationship between the groceries we buy and the food we eventually consume. This relationship is evident, irrespective of whether purchases are made by individuals or collectively by family members. The correlation between food purchases and consumption is critical to understanding dietary habits. While the connection may not be perfect due to various factors such as waste and sharing, it becomes more pronounced and reliable as we examine data from larger groups of people. For example, if we assume that the match between what is bought and what is consumed is about 75%, we face a 25% uncertainty for an individual or a single purchase. However, as we compile data from more people or transactions, this uncertainty diminishes exponentially. The formula 25/100^X, where X represents the number of observations (individuals or family purchases), shows how the uncertainty decreases with larger datasets, approaching negligible levels very quickly.
This method of analysis doesn't hinge on the assumption that a single person is responsible for all grocery shopping within a household. Instead, it considers the collective buying behavior of all household members, offering a more comprehensive view of consumption patterns. This approach allows for a more accurate analysis, as it incorporates the diverse dietary needs and preferences within a family. For instance, we can analyze the aggregate data of purchases made by all members of a household, including children and adults, to get a clearer picture of the household's overall dietary habits. Furthermore, by examining purchases from a broader perspective, we can apply sophisticated data analysis techniques to uncover nuanced insights into consumption patterns, even in complex household structures. This approach leverages the power of big data to provide a deeper understanding of nutritional trends and behaviors, thereby enhancing the quality of dietary research and informing better public health policies.
In many countries, the transition to digital healthcare records has revolutionized the way medical information is stored and accessed. This digitalization offers an unprecedented opportunity to conduct comprehensive statistical analyses on the relationship between food consumption patterns and health outcomes. By integrating anonymized grocery purchase data with anonymized healthcare information, researchers can delve deep into the impacts of dietary habits on health at a population level. This approach ensures privacy and confidentiality, as the data is stripped of personal identifiers before being processed by research algorithms. Such an integrated analysis could uncover vital insights into nutritional epidemiology, revealing trends and associations that inform public health policies and dietary recommendations. The anonymity of data delivery to research algorithms not only safeguards individual privacy but also facilitates a more nuanced understanding of the complex interactions between diet and health, potentially leading to breakthroughs in preventive medicine and personalized nutrition strategies.
This method represents a paradigm shift towards continuous, evolving research, a marked departure from the static nature of most nutritional studies currently published. By leveraging real-time, anonymized data streams from both grocery purchases and healthcare records, this approach enables an ongoing analysis that can adapt and refine its hypotheses in response to emerging trends and data patterns. Unlike traditional studies that offer a snapshot based on data collected at a specific point in time, this dynamic model of research benefits from accumulating vast datasets over time, enhancing the reliability and depth of its findings. This continuous feedback loop means that as more data becomes available, the research can incorporate these new insights, allowing for the adjustment of variables and the exploration of new questions. Consequently, this approach not only provides more accurate and up-to-date insights into the relationship between diet and health but also progressively improves its predictive power and relevance, setting a new standard for nutritional science research in the digital age.
Health promoting policies
Easy accessibility and overindulgence in carbohydrates, especially the refined and processed kinds like sugar and white flour, is frequently associated with obesity. These categories of carbohydrates are swiftly metabolized, leading to rapid surges in blood sugar levels. This rapid digestion often results in immediate hunger pangs following a meal, thereby promoting overconsumption that ultimately leads to weight gain.
The contemporary culinary landscape is typically dominated by high-calorie, carbohydrate-dense offerings like fast food and pre-packaged snacks. These food items, usually teeming with added sugars and offering sparse nutritional value, are often viewed as inexpensive and effortless options. As a result, they are readily available to consumers. This easy access can inadvertently encourage an excessive intake of carbohydrates, which in turn, could pave the way to obesity.
Conversely, research has indicated that protein plays a pivotal role in creating a sense of long-lasting satiety compared to carbohydrates. By embracing a dietary regimen abundant in protein and deficient in processed carbohydrates, it's possible to suppress persistent hunger pangs. This, in turn, can pave the way for weight reduction and the cultivation of healthier eating behaviors.
Advocating for the widespread accessibility of foods abundant in proteins, like legumes, alongside carbohydrates that take longer to digest, could drastically impart a positive influence on public health. Simultaneously, efforts should be made to curtail the omnipresence of calorie-dense, rapidly digestible carbs. A nutritional regimen that's high in protein but low in refined carbohydrates can suppress hunger pangs, facilitate weight reduction, and amplify the overall state of health.
Chock-full of protein and having a relatively low environmental footprint, legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas are a sustainable food source. They require fewer resources to grow compared to many other crops. Furthermore, they possess the unique ability to convert airborne nitrogen into a usable form, mitigating the need for artificial fertilizers.
Incorporating whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your diet, which are rich in slowly digestible carbohydrates, can offer numerous health benefits. These include maintaining steady blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of chronic ailments, and promoting a sense of satiety. On the other hand, a dietary pattern dominated by calorie-dense, quick-digesting carbohydrates like sugar and refined flour could lead to weight gain and elevate the risk of chronic conditions.
A comprehensive policy intent on revolutionizing our food system must consider more than just the nutritional value of our food. It must also probe into the toxicity levels and environmental footprint of food production. The misuse of pesticides and neglectful agricultural methods pose a dual threat to our well-being and the environment. Consequently, the policy should incorporate the following elements:
- Introducing financial rewards for farmers who embrace sustainable farming techniques, especially those growing legumes. This would discourage the use of harmful pesticides and lessen the environmental footprint.
- Imposing stricter regulations and monitoring mechanisms on food production processes, particularly focusing on toxicity levels and environmental implications. These controls should be strongly underpinned by enforceable laws.
- Advocating for supermarkets and retailers to diversify their stock, emphasizing legumes and other plant-based protein sources. This would make healthier, more environmentally friendly options readily available to the public.
- Leveraging AI technology to oversee and manage food supply chains. This can ensure reduced toxicity levels, environmental impact, and waste by accurately predicting demand and allocating resources efficiently.
- Informing consumers about the nutritional benefits of a diet abundant in legumes and carbohydrates that are slowly digestible. The focus should be on the long-term health benefits that such a diet can provide.
- Enforcing taxes or limitations on highly processed foods that are rich in rapidly digestible carbs as a way to discourage overconsumption. With the successful execution of these policies, we can significantly enhance public health by curbing the rising tide of obesity and related chronic diseases. Concurrently, we can promote more sustainable and green farming practices. AI stands to be a key player in supervising these systems, ensuring adherence, and assisting in creating an efficient, waste-minimizing supply chain. The result would be a food system that promotes our health, supports our farmers, and respects our planet.
Disease control policies
Embarking on the journey to develop new pharmaceuticals is a formidable venture. It is expensive, intricate, and time-consuming, typically requiring a span of years to carry out comprehensive research, clinical trials, and ultimately securing regulatory approval. The escalating cost of launching a new drug into the market since the 1970s can be largely attributed to the demanding requirements of animal testing and clinical trials. The dramatic rise in costs can be traced back to several significant events, one of which includes the infamous case of Thalidomide, a sleep-inducing medication introduced in 1957 that was later discovered to induce severe birth malformations. As a result, the average expenditure for creating a new drug has seen a meteoric rise, escalating from 179 million USD in the 70s to a staggering 2558 million USD in the 2000s.
The soaring costs associated with drug development can often deter investments in the creation of novel treatments targeting uncommon ailments or those drugs meant to serve as the final line of defense in antibiotic therapy. Despite the existence of around 7,000 rare diseases that cumulatively impact an estimated 400 million individuals globally, the majority of these conditions remain without effective treatment options or known cures. The limited medications that are on the market for these diseases are frequently priced beyond the reach of most patients.
Antibiotics of last resort are crucial in combating infections that stem from bacteria impervious to most other antibiotic treatments. Yet, the small patient base for such drugs dampens their commercial viability, creating a risk of potential shortages in these life-saving medications.
Tackling these issues calls for a united front from both governmental bodies and private enterprises. The initiation of state-backed programs can stimulate the creation of novel antibiotics and therapies for uncommon ailments. This not only caters to the public health demands but also makes these projects financially viable, even if they may not seem profitable solely based on market trends.
Artificial intelligence (AI) may revolutionize the field of disease control policies. AI holds the promise to enhance drug development procedures, consequently minimizing expenses and accelerating the time to market. Moreover, it could foster a more individualized approach to healthcare, providing crucial knowledge for formulating treatments for uncommon diseases, and facilitating the invention of new antibiotics.
To encapsulate, the amalgamation of public financial support and state-of-the-art technologies such as Artificial Intelligence holds the potential to guarantee that no group of patients, regardless of their size, is overlooked in our relentless quest for enhanced healthcare.
Drug policies
Drug prohibition laws draw heavily upon the fundamental economic concept of supply and demand - an explanation of how product pricing is dictated by the interplay of availability and consumer interest. Such laws are designed with the intent to limit access to drugs by making their production, distribution and consumption illegal. The enforcement of these laws generally results in a decrease in the drug supply, leading to a surge in drug prices, assuming the demand stays steady.
The paradox of drug prohibition is a noteworthy one. The very measures taken to curtail drug accessibility, ostensibly to reduce harm, may unintentionally foster lucrative fiscal lures for lawbreakers. With the escalation in drug prices comes the prospect of increased profits from the shadowy world of illicit drug trafficking. This triggers a vicious cycle: the more that is spent on implementing drug prohibition laws, the more lucrative the black market for drugs becomes, as long as the demand for narcotics continues. This circumstance highlights the complex challenges and inherent restrictions when relying solely on law enforcement to mitigate drug consumption and its concomitant societal detriments.
The U.S.'s long-standing 'war on drugs' has seen an astronomical expenditure of trillions of dollars since it began, with an unfortunate increase in drug addiction rates in the country rather than a decline. Moreover, this strategy has ushered in a dramatic surge in incarceration rates by a shocking 500%. A comprehensive 2011 report by The Global Commission on Drug Policy declared this war on drugs as a definitive failure, strongly advising a halt to the criminalization of drug consumption.
In a context where recreational drugs have been approved for use, it is crucial to establish a well-calibrated equilibrium between taxation and regulation. Exorbitant tax rates and overbearing regulations can unintentionally fuel the illicit drug market, a scenario that can be as damaging to society as the misuse of drugs. The underground drug trade is fraught with its unique perils. Therefore, maintaining tax and regulatory policies that are firm yet fair could encourage most drug transactions to remain within the bounds of legality.
Granting legal status to drugs can pave the way for the imposition of strict manufacturing criteria, akin to those dictated for pharmaceutical drugs; this ensures the safety of the product. Additionally, it also opens up the possibility for compulsory labeling requirements, thus equipping consumers with information regarding the components of the drug as well as any associated risks. Conversely, drugs procured from the black market often come with their own set of dangers; they may contain detrimental impurities and usually do not carry any informative labels, thereby exposing users to increased risk.
The concept of a harm reduction strategy underpins the proposition that drug taxation and regulation should align with their respective harm impacts. This strategy recognizes the intricate nature of drug-related issues and the insufficiency of universal remedies to address the multitude of challenges stemming from drug consumption. Rather than exclusively concentrating on curtailing or eradicating drug use, a harm reduction strategy gives precedence to mitigating the detrimental repercussions linked to drug consumption.
A comprehensive strategy for managing drugs can be put into action by instituting regulations and levying taxes proportional to the scientifically proven harm they inflict. This approach demands a thorough assessment of drugs, taking into account diverse elements such as their potential for addiction, risk of overdose, and potential adverse impacts on both mental and physical health. As a result, drugs that are identified as more harmful would be subjected to increased taxation and tighter regulations. On the other hand, substances that are less harmful would be met with reduced taxes and more relaxed regulations.
A system of this nature holds the potential to bring about a wide array of advantages. By making less harmful substances readily available at affordable prices, it could significantly curb the detrimental effects associated with drug use and simultaneously generate funds for programs aimed at harm reduction and public health interventions. Furthermore, the establishment of a legal, regulated marketplace for drugs could contribute to a decrease in illicit drug trade and the criminal activities it fuels.
In 2006, the UK Science and Technology Select Committee embarked on a mission to reassess the existing drug classification system, an initiative commissioned by the UK government. This endeavor, detailed in the Committee's drug categorization report, involved a meticulous examination of the scientific evidence pertaining to the harm inflicted by various drugs. The ultimate objective of this investigative report was to put forth a more logical, evidence-grounded system for drug classification.
The committee's investigation revealed that the current categorization system, which originates from the 1971 Misuse of Drugs Act, does not provide an accurate assessment of the harm levels associated with different drugs. The committee found an overestimation of harm for substances such as cannabis, ecstasy, LSD, and magic mushrooms when compared to existing evidence. On the other hand, it underlined that the damage potential of substances like tobacco, alcohol, crack, and heroin was underestimated in the current classification.
The study proposed a revised system for drug classification, one that takes a multifaceted approach factoring in variables such as potential for addiction, overdose risk, and possible detrimental effects on both mental and physical wellbeing. In addition to this, the report advocates for the establishment of a novel, independent scientific institution. This entity's primary function would be to scrutinize and evaluate the harm induced by various drugs, subsequently providing recommendations for their classification.
The study contended that imposing criminal penalties for drug use and possession has not demonstrated a significant decrease in drug usage or associated damages. Instead, it promoted a public health-centric strategy, aiming to minimize harm. This viewpoint was reinforced by a comprehensive 2010 report from the Independent Scientific Committee on Drugs. Moreover, a 2006 analysis of recreational drugs' toxicity revealed that the likelihood of overdosing on ethanol is roughly a hundredfold greater than illegal substances such as cannabis, LSD, and psilocybin mushrooms.
Law enforcement policies
Establishing a worldwide law enforcement body could be a key solution in combating grave human rights violations, including genocide. This international organization would have the power to step in when nation-states are either reluctant or unable to act. Such intervention could serve as a protective shield for susceptible communities against horrific acts, and potentially prevent the worsening of conflicts. Nevertheless, the creation of a global police force is not without its hazards.
A significant concern is the possibility of fatal encounters, which could occur when law enforcement officers are compelled to use force to safeguard the public and reestablish peace. To alleviate this risk, officers must undergo comprehensive training in the utilization of non-lethal weaponry. Moreover, they must strictly adhere to established guidelines and protocols when resorting to force.
One of the potential hazards linked with an international law enforcement body is the possibility of exploitative surveillance practices. There's a risk that officers may resort to surveillance techniques that violate individual privacy rights and encroach on civil liberties. To mitigate this risk, the creation of a worldwide data protection watchdog could prove advantageous. This body could provide ongoing oversight of all police surveillance operations, ensuring they adhere to the guidelines set by international human rights standards.
In addition to the aforementioned strategies, it's vital to establish a system of supervision and accountability to assure the moral integrity and effectiveness of the worldwide law enforcement body. This mechanism could incorporate an autonomous supervisory committee composed of representatives drawn from civil society along with other pertinent stakeholders. The role of this committee would be to monitor the activities of the police force while proposing potential enhancements.
Military policies
The future of warfare is likely to see a significant shift towards the utilization of advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems. These AI systems will play a crucial role in analyzing communication traffic within an enemy's governing system. By meticulously scrutinizing the flow of data, messages, and commands, the AI will be able to identify the most critical nodes in the communication network. These nodes represent the vital points through which information is disseminated and decisions are communicated; they are the linchpins that keep the enemy's command and control structure operational.
Once these pivotal nodes are identified, the AI will proceed to the next phase of its operation: strategizing the most effective ways to neutralize them. This is where the concept of using high-altitude crafts comes into play. These crafts, operating at altitudes beyond the reach of conventional anti-air defenses, will be equipped with precision-guided intelligence high-speed rockets. These rockets, characterized by their swift and agile flight capabilities, will be tasked with the mission of striking the identified nodes.
The aim here is to dismantle the enemy's communication network at its most vulnerable points. By knocking out these nodes, the AI-driven strategy would disrupt the flow of information, sow confusion, and cripple the enemy's ability to coordinate and respond effectively. This approach represents a blend of cutting-edge technology and tactical ingenuity, leveraging AI's analytical prowess and the precision of modern weaponry to achieve strategic advantages in the realm of future warfare.
The advancement of AI in warfare, particularly in its ability to disrupt and neutralize critical communication nodes of an enemy, brings a significant shift in how conflicts are approached and managed. This technology, while potent and potentially transformative in the field of military operations, poses a nuanced impact on different segments of the population.
For ordinary people, especially those who are not directly involved in maintaining or supporting what could be considered malevolent power structures, there is a lesser reason to fear. These AI-driven strategies and technologies are primarily designed to target specific military and strategic assets, not civilians. Their use is often governed by strict rules of engagement and ethical considerations, ensuring that the impact on ordinary lives is minimized. In this way, the focus of such technologies is on weakening the command, control, and communication capabilities of the adversary, rather than causing indiscriminate harm.
However, individuals who are actively involved in maintaining or operating within these adversarial power structures may find themselves at greater risk. Given that these AI systems are specifically designed to identify and neutralize key nodes and components critical to the functioning of these structures, those associated with them could be directly impacted. It's a scenario where the precise and targeted nature of the technology could disrupt their operations, communication, and overall strategic capabilities.
This distinction highlights the importance of precision and ethical considerations in modern warfare. The aim is to mitigate the impact on civilians and focus on degrading the military and strategic capabilities of an adversary, thereby potentially leading to a quicker resolution of conflicts with fewer casualties and collateral damage.
Immigration policies
The social, economic, and cultural landscape of a country is deeply molded by its immigration policy. Designing a potent immigration strategy demands a nuanced equilibrium. This balance considers the intertwining of national and local interests, the fulfillment of economic requirements, the provision of security, the adherence to humanitarian responsibilities, and the acknowledgement of the advantages brought about by a globalized society.
At the grassroots level, it is vital for communities within various regions to have a platform to express their perspectives and apprehensions about immigration, exercising a degree of control over the influx of newcomers in order to maintain societal equilibrium. It is crucial for immigration policies to be attuned to potential repercussions on aspects such as employment, public services, and cultural identity. This ensures that the pace and character of immigration are in sync with a community's capacity for assimilation.
In circumstances of urgency, like a sudden influx of refugees, the importance of international cooperation intensifies. It's unjust for a single region to shoulder the weight of a global crisis. Therefore, it's imperative for nations to unite and establish systems that facilitate a fair and efficient division of duties. By doing so, we ensure the rights and well-being of those swept up in these crises are safeguarded.
At the same time, it's important not to underestimate the advantages of a globally inclusive society. The unrestricted movement of individuals can spark economic expansion, inspire innovation, and foster cultural plurality. Immigrants frequently introduce distinctive abilities and viewpoints, acting as engines for economic progression and cultural enhancement in their new communities. Furthermore, it offers individuals the chance to pursue improved living conditions and cultivates a sense of global empathy and collaboration.
In the age of rapid globalization and unprecedented technological progress, it's crucial to develop immigration policies that are adaptable and react promptly to shifting scenarios. It's incumbent on policy makers to engage in ongoing conversations with a variety of stakeholders, leverage data to inform their decisions, and explore innovative strategies such as using AI-enabled systems. These systems can offer useful insights into migration trends and facilitate more efficient management of processes.
References
- ↑ M. Woolhouse, F. Scott, Z. Hudson, R. Howey, and M. Chase-Topping, “Human viruses: discovery and emergence,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, vol. 367, pp. 2864–2871, Oct. 2012.
- ↑ J. Davies and D. Davies, “Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance,” Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., vol. 74, pp. 417–433, Aug. 2010.
- ↑ J. Owen, “Farming claims almost half earth,” National Geographic, 2005
- ↑ Water footprint network, “Water footprint.” http://waterfootprint.org/en/resources/water-footprint-statistics/